Are you tired of hearing about "good" and "bad" fats, feeling lost in the sea of information about cholesterol? It's time to cut through the confusion and discover the power of one particular type of fat that can actuallyhelpimprove your cholesterol levels and boost your heart health. Prepare to unlock the secrets of monounsaturated fats!
Navigating the world of fats and cholesterol can feel overwhelming. You might be struggling to understand which foods to embrace and which to avoid. Perhaps you're concerned about the impact of your diet on your long-term health, especially regarding heart disease. The conflicting advice out there only adds to the frustration, leaving you unsure of the best path forward.
The purpose of this article is to equip you with the knowledge you need to understand monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) and how they can positively influence your cholesterol levels. We'll explore what MUFAs are, where to find them, and how to incorporate them into your diet for a healthier heart.
In this article, we've explored the potential benefits of monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) for managing cholesterol and promoting heart health. We delved into the types of foods rich in MUFAs, such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts. By incorporating these healthy fats into your diet, you can potentially lower your LDL ("bad") cholesterol and raise your HDL ("good") cholesterol. Keywords: monounsaturated fats, cholesterol, heart health, olive oil, avocados, nuts, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, diet, healthy fats.
Monounsaturated Fats: My Journey to Understanding
My journey with understanding the importance of monounsaturated fats for cholesterol started a few years ago when my doctor expressed concern about my slightly elevated LDL cholesterol levels. Like many, I initially panicked and envisioned a future filled with tasteless, restrictive meals. I started researching, and that's when I stumbled upon the wealth of information surrounding MUFAs. I learned that these fats, found in delicious foods like avocados and olive oil, could actually help improve my cholesterol profile! This was a game-changer. I began experimenting with recipes, swapping out saturated fats for MUFAs whenever possible. Instead of butter, I drizzled olive oil on my vegetables. I snacked on almonds instead of processed chips. Slowly but surely, I saw a positive change in my cholesterol numbers. Incorporating MUFAs wasn't just about restriction; it was about making smarter, tastier choices that benefitted my health. The goal is to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase HDL (good) cholesterol, improving the overall cholesterol ratio. Foods rich in monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds are beneficial for maintaining cardiovascular health. MUFAs can also help reduce inflammation, a key factor in heart disease. Making these simple dietary swaps has not only improved my numbers, but also my overall sense of well-being, showing the real power of understanding and utilizing monounsaturated fats for heart health. This helped in decreasing chances of cardiovascular related diseases.
What Are Monounsaturated Fats?
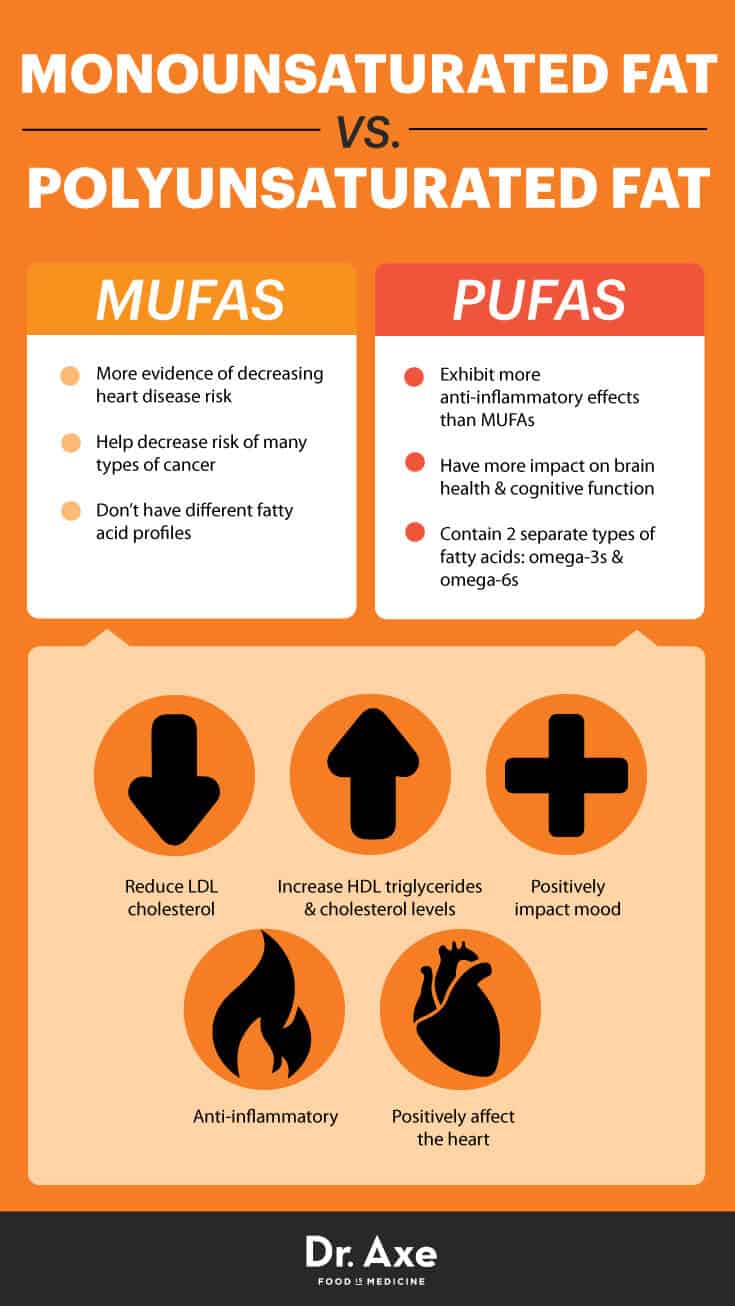
Monounsaturated fats, or MUFAs, are a type of unsaturated fat molecule that have one double bond in their chemical structure. This structure distinguishes them from saturated fats, which have no double bonds, and polyunsaturated fats, which have multiple double bonds. This seemingly small difference in chemical structure makes a big difference in how our bodies process these fats. MUFAs are generally liquid at room temperature and are considered "healthy" fats because of their potential benefits for heart health. They play a crucial role in maintaining cell membranes and supporting hormone production. When you consume MUFAs in place of saturated or trans fats, you can potentially lower your LDL cholesterol levels, which reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke. Key sources of MUFAs include olive oil, avocados, almonds, pecans, hazelnuts, and canola oil. Incorporating these foods into your daily diet can provide a steady source of these beneficial fats. Moreover, MUFAs can also improve insulin sensitivity, which can aid in blood sugar control, especially important for those with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. Understanding the structure and function of MUFAs empowers you to make informed dietary choices that support your overall well-being. The health benefits can also be boosted when eating together with other healthy food groups.
The History and Myths of Monounsaturated Fats
The history of understanding monounsaturated fats is intertwined with the broader evolution of nutritional science. For many years, dietary fats were largely demonized, with a broad brushstroke approach that failed to differentiate between different types of fats. Saturated fats, in particular, were seen as the primary culprit for heart disease, leading to recommendations to drastically reduce overall fat intake. However, as research progressed, scientists began to recognize the nuances of dietary fats. The Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil (a primary source of MUFAs), gained attention for its association with improved heart health and longevity. This led to a re-evaluation of the role of fats in our diet and the recognition that some fats, like MUFAs, could actually be beneficial. One common myth is that all fats are bad for you and should be avoided. This stems from the initial misconception about dietary fats and their impact on heart health. Another myth is that olive oil is the only source of MUFAs. While olive oil is an excellent source, avocados, nuts, and seeds also offer significant amounts. It’s also sometimes believed that you can eat unlimited amounts of MUFAs. Like all nutrients, moderation is key, and it's important to balance MUFA intake with other healthy food choices. Understanding the history and dispelling the myths surrounding MUFAs allows you to make informed choices and incorporate these beneficial fats into your diet with confidence. One should always be aware of the source and to have the best effect.
The Hidden Secret of Monounsaturated Fats
The "hidden secret" of monounsaturated fats isn't really a secret at all, but rather a benefit that often gets overlooked: their ability to improve insulin sensitivity. While their role in lowering LDL cholesterol is well-known, MUFAs also play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin, is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown that replacing saturated fats with MUFAs can improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for your body to use glucose for energy and preventing blood sugar spikes. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with prediabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes. By incorporating MUFA-rich foods into your diet, you're not just improving your cholesterol profile; you're also taking proactive steps to prevent diabetes and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. This dual benefit makes MUFAs an especially valuable component of a heart-healthy and diabetes-friendly diet. Another often-unmentioned advantage is their role in satiety. MUFAs can help you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight management by reducing overall calorie intake. This helps in managing a healthy blood sugar.
Recommendations for Monounsaturated Fats
So, how much monounsaturated fat should you be aiming for in your diet? Experts generally recommend that MUFAs make up a significant portion of your total daily fat intake. A good guideline is to aim for around 15-20% of your daily calories from MUFAs. However, it's important to remember that this is just a general recommendation, and individual needs may vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health. The best way to determine your optimal MUFA intake is to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations. When incorporating MUFAs into your diet, focus on choosing whole, unprocessed foods such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds. These foods not only provide MUFAs but also offer a wealth of other beneficial nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Be mindful of portion sizes, even with healthy fats. While MUFAs are beneficial, they are still calorie-dense, so overconsumption can lead to weight gain. Aim for small, regular portions throughout the day. For example, use a tablespoon of olive oil for cooking, add a quarter of an avocado to your salad, or snack on a handful of almonds. These additions can provide a steady supply of MUFAs without overdoing it on calories. It's important to consider individual calorie intake and to not exceed beyond the daily recommended calories intake.
The Role of Olive Oil in Monounsaturated Fats
Olive oil is often celebrated as a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet and a fantastic source of monounsaturated fats (MUFAs). It's extracted from olives and contains oleic acid, a type of MUFA known for its potential health benefits. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is the highest quality, least processed form of olive oil, and it's packed with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, in addition to MUFAs. These antioxidants, like polyphenols, can further contribute to heart health by protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation. When selecting olive oil, opt for EVOO whenever possible. Look for a dark glass bottle, as light can degrade the oil's quality. Also, check the harvest date to ensure freshness. Olive oil is incredibly versatile in the kitchen. You can use it for cooking, sautéing, roasting, and even baking. It's also delicious drizzled over salads, vegetables, or grilled meats. When cooking with olive oil, be mindful of the smoke point. While EVOO has a relatively high smoke point, it's best to avoid overheating it, as this can damage the oil and reduce its beneficial properties. You can also consume it raw for maximum benefit. Remember that olive oil is still a fat source, so use it in moderation. A tablespoon or two per day is generally sufficient to reap its health benefits. Incorporating olive oil into your diet is a simple and delicious way to increase your MUFA intake and support your heart health. Using it with high intensity will change its properties.
Tips for Incorporating Monounsaturated Fats
Making small, gradual changes to your diet is the most sustainable way to incorporate more monounsaturated fats. Start by swapping out saturated and trans fats for MUFA-rich options. For example, use olive oil instead of butter or lard for cooking. Choose avocado instead of mayonnaise on sandwiches. Snack on nuts and seeds instead of processed snacks. Don't be afraid to experiment with new recipes and cuisines that feature MUFA-rich ingredients. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, is a great source of inspiration, with its emphasis on olive oil, vegetables, and lean protein. Get creative with your salad dressings. Instead of store-bought dressings, which are often high in saturated fat and sugar, make your own using olive oil, vinegar, and herbs. You can also add avocado or nuts to your salads for an extra boost of MUFAs. Be mindful of portion sizes, even with healthy foods. Nuts and seeds, for example, are calorie-dense, so stick to a small handful as a snack. Avocados are also relatively high in calories, so limit yourself to a quarter or half of an avocado per serving. Read food labels carefully to identify sources of saturated and trans fats and make informed choices. Choose products that are low in saturated fat and free of trans fats. Small and consistent steps is always a good start to change your eating habits. Understanding the correct calorie intake and food ratio helps with this diet.
Pairing MUFAs with Other Healthy Foods
The benefits of monounsaturated fats are amplified when they're combined with other healthy foods. For example, pairing MUFA-rich foods with fiber-rich foods can further improve cholesterol levels and promote digestive health. Fiber helps to bind cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Eating MUFAs with lean protein sources can also contribute to satiety and weight management. Protein helps you feel fuller for longer, which can reduce overall calorie intake. Excellent sources of lean protein include fish, poultry, beans, and lentils. Consider adding olive oil to your salads or vegetables, then add in a protein such as chicken or fish. Make sure to add in fiber rich foods for the best results. Also, consider cooking it with a good style so that the texture is maintained. Pairing avocados with whole-grain toast can also provide a balanced and satisfying meal. When planning your meals, aim for a combination of MUFAs, fiber, and lean protein to maximize the health benefits. By combining different nutrient-rich foods, you can create a synergistic effect that supports your overall well-being. In combination of the correct nutrients will make you healthy and strong.
Fun Facts About Monounsaturated Fats
Did you know that the word "monounsaturated" refers to the chemical structure of the fat molecule? The "mono" indicates that there is only one double bond in the carbon chain, while "unsaturated" refers to the fact that the carbon atoms are not fully saturated with hydrogen atoms. Olive oil, a primary source of MUFAs, has been used for centuries in cooking, medicine, and even religious ceremonies. Avocados, another MUFA powerhouse, were once considered a luxury food and were reserved for the wealthy. Nuts and seeds, which are also rich in MUFAs, have been a staple food for humans for thousands of years, providing essential nutrients and energy. The Mediterranean diet, known for its emphasis on olive oil and MUFA-rich foods, is consistently ranked as one of the healthiest diets in the world. MUFAs are not only beneficial for heart health but also play a role in brain function and cognitive health. They help to maintain the structure and function of brain cells, which is essential for optimal cognitive performance. Learning about the history and trivia surrounding MUFAs can make them more interesting and engaging, motivating you to incorporate them into your diet. In addition, it helps in improving mind conditions and overall health. The knowledge of fats will guide you to become a healthy being.
How to Incorporate Monounsaturated Fats
Incorporating monounsaturated fats into your diet doesn't have to be complicated or time-consuming. Start by making small, simple swaps in your everyday meals and snacks. Use olive oil instead of butter or vegetable oil for cooking. Add avocado slices to your sandwiches or salads. Snack on a handful of almonds or walnuts instead of processed chips or crackers. Make your own salad dressings using olive oil, vinegar, and herbs. Drizzle olive oil over roasted vegetables or grilled meats. Experiment with new recipes that feature MUFA-rich ingredients, such as Mediterranean dishes or avocado toast. Choose lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, beans, and lentils to complement your MUFA intake. Be mindful of portion sizes, even with healthy foods. MUFAs are still calorie-dense, so use them in moderation. Read food labels carefully to identify sources of saturated and trans fats and choose products that are low in these unhealthy fats. Shop consciously and prefer whole foods in their natural state. The goal is to make these swaps naturally into our diet. Understand that this is a lifestyle change and not a short term measure. As one continues to eat healthy food then one will start to feel healthy.
What If You Don't Get Enough Monounsaturated Fats?
While it's difficult to pinpoint a specific deficiency of monounsaturated fats, consistently low intake can have several potential consequences. You might not experience immediate or dramatic symptoms, but over time, a lack of MUFAs can negatively impact your heart health and overall well-being. Without sufficient MUFAs, your LDL cholesterol levels may remain elevated, increasing your risk of heart disease. You may also experience increased inflammation, which can contribute to a variety of health problems, including arthritis, diabetes, and cancer. A lack of MUFAs can also affect your brain function, as these fats are essential for maintaining the structure and function of brain cells. You may experience cognitive decline, memory problems, or mood swings. Insufficient MUFA intake can also impact your skin health, leading to dryness, irritation, and premature aging. Finally, a lack of MUFAs can contribute to nutrient deficiencies, as these fats help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. However, it is important to understand the amount that can be consumed daily. Excessive consumption of monounsaturated fat can lead to obesity.
List of Foods Rich in Monounsaturated Fats
To increase your intake of monounsaturated fats, focus on incorporating these foods into your diet:
- Olive oil: Use it for cooking, salad dressings, and drizzling over foods.
- Avocados: Add them to salads, sandwiches, or smoothies.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, pecans, hazelnuts, and cashews are all good sources.
- Seeds: Sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, and pumpkin seeds contain MUFAs.
- Olives: Enjoy them as a snack or add them to salads and pasta dishes.
- Canola oil: Use it for cooking and baking.
- Peanut oil: Use it for frying and sautéing.
- High-oleic sunflower oil: Use it for cooking and baking.
- Almond butter: Spread it on toast or use it in smoothies.
- Peanut butter: A good source of MUFAs, but choose natural varieties without added sugar and salt.
Be aware of food source and calorie count.
Question and Answer
Q: How do monounsaturated fats affect cholesterol?
A: Monounsaturated fats can help lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels and raise HDL ("good") cholesterol levels, improving your overall cholesterol profile.
Q: Are all types of olive oil equally beneficial?
A: Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is the highest quality and offers the most health benefits due to its high antioxidant content.
Q: Can I eat too many monounsaturated fats?
A: Yes, even healthy fats should be consumed in moderation, as they are still calorie-dense. Aim for 15-20% of your daily calories from MUFAs.
Q: Can I cook with olive oil at high temperatures?
A: While EVOO has a relatively high smoke point, it's best to avoid overheating it, as this can damage the oil and reduce its beneficial properties. For high-heat cooking, consider using refined olive oil.
Conclusion of Monounsaturated Fats for Cholesterol
Monounsaturated fats are a valuable tool in the fight against high cholesterol and heart disease. By understanding what they are, where to find them, and how to incorporate them into your diet, you can take proactive steps to improve your health and well-being. Remember to focus on whole, unprocessed foods, choose healthy cooking methods, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. Embrace the power of MUFAs and pave the way for a healthier, happier heart!